Surveillance and updates for chikungunya virus disease

Seasonal surveillance in the EU/EEA for 2025
Update providing weekly overview of the countries and areas where chikungunya virus disease cases have been reported.
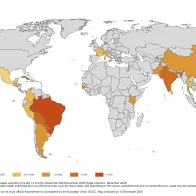
Monthly updated overview of the worldwide transmission of chikungunya

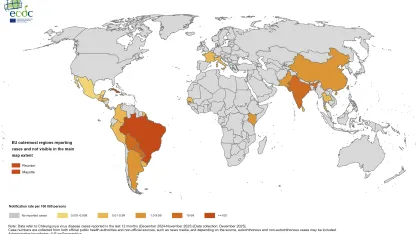
Travel-associated cases in the EU/EEA
This page displays the places where reported travel-associated chikungunya cases are likely to have been infected.
Reports
Read more
Scientific journal article
Scientific journal article