Chikungunya virus disease
Chikungunya is a viral disease that mosquitoes can pass to humans. The name 'chikungunya' comes from the way patients often bend over in pain.
The most common symptoms are fever, muscle and joint pain, and a rash. Most people recover, but 30-40% of those affected may develop chronic arthritis that can last for months or even years.
The time it takes for symptoms to appear from being infected can vary. It can take up to 12 days, with an average of 3 to 7 days.
Certain factors can increase the risk of having a more severe form of the disease. These include:
- being in the last weeks of pregnancy (for babies exposed during childbirth)
- being over 65 years old
- having other health problems (co-morbidities)
For older people, joint pain can turn into a long-lasting rheumatoid arthritis condition. Newborns can have meningoencephalitis, which affects the brain.
Although it is generally not considered a deadly disease, in some cases, there have been deaths linked to the virus (mostly in people with existing medical conditions).
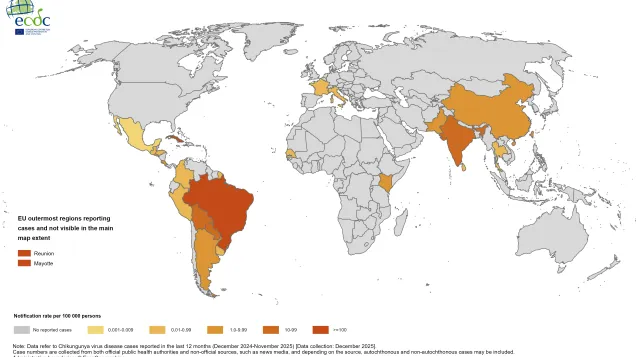
Chikungunya virus disease is spread by mosquitoes, particularly Aedes mosquitoes, which mainly bite people outdoors.
Since there are no specific antiviral drugs for chikungunya, the treatment focuses on managing the symptoms. This includes using pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medicines.
After recovering from chikungunya, a person is likely to have lifelong immunity against future chikungunya virus infections and is less likely to get it again in the future.
There are vaccines available to help protect adults and adolescents against the disease..
For individuals, protective measures include:
- using mosquito repellent
- the use of mosquito nets
- sleeping or in screened or air-conditioned rooms
- wearing clothing that cover most of the body.
Preventative measures also focus on controlling the mosquitoes that spread the virus.
Some ways to reduce mosquito breeding sites include:
- Regularly removing or treating open containers with stagnant water, like flowerpots, tires, tree holes, and rock pools.
- Ensuring water containers, barrels, wells, and storage tanks are well covered.
During outbreaks, aerial spraying of insecticides can be used to get rid of adult mosquitoes and mitigate the spread of the disease.
Featured