Epidemiological update: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV)
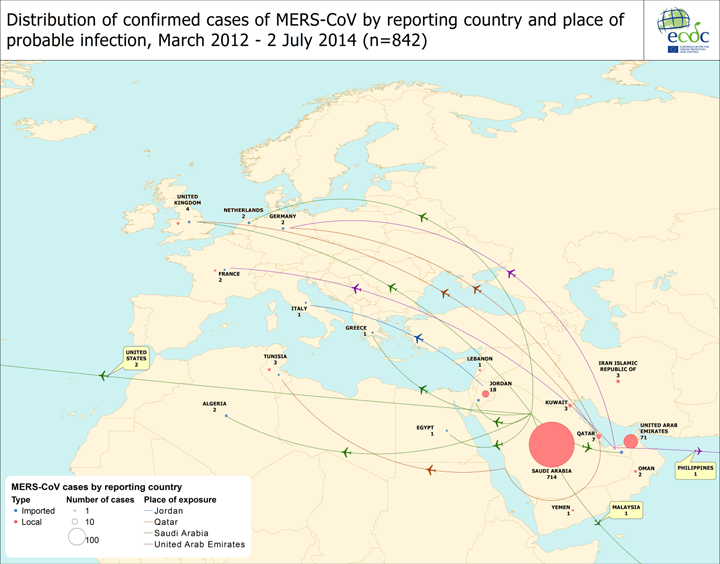
Since April 2012 and as of 2 July 2014, overall 842 cases of MERS-CoV infection have been reported by local health authorities worldwide, including 322 deaths.
Since April 2012 and as of 2 July 2014, overall 842 cases of MERS-CoV infection have been reported by local health authorities worldwide, including 322 deaths.Between 4 June 2014 and 2 July 2014, health authorities in Saudi Arabia reported 25 cases of MERS-CoV, health authorities in the United Arab Emirates one case and the Iranian health authorities one case, showing a decline in the number of cases (Figure 1).
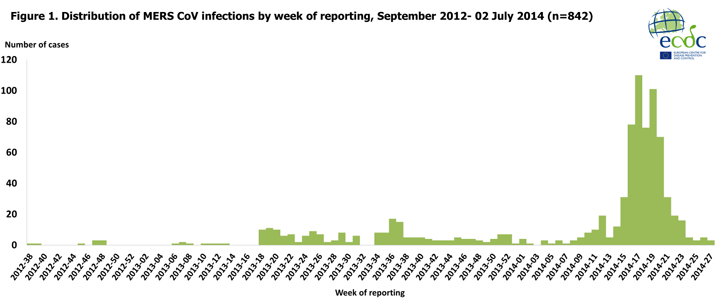
Table 1. Confirmed cases, deaths and date of onset for the most recent case, by region, as of 2 July 2014
Region/country |
Cases |
Deaths |
Date of onset/reporting for most recent case |
|---|---|---|---|
Middle East | |||
Saudi Arabia |
714 |
292 |
01/07/2014 |
United Arab Emirates |
71 |
9 |
11/06/2014 |
Qatar |
7 |
4 |
04/11/2013 |
Jordan |
18 |
5 |
23/05/2014 |
Oman |
2 |
2 |
20/12/2013 |
Kuwait |
3 |
1 |
07/11/2013 |
Egypt |
1 |
0 |
22/04/2014 |
Yemen |
1 |
1 |
17/03/2014 |
Lebanon |
1 |
0 |
22/04/2012 |
Iran |
3 |
1 |
27/05/2014 |
Europe | |||
UK |
4 |
3 |
06/02/2013 |
Germany |
2 |
1 |
08/03/2013 |
France |
2 |
1 |
08/05/2013 |
Italy |
1 |
0 |
31/05/2013 |
Greece |
1 |
0 |
08/04/2014 |
Netherlands |
2 |
0 |
05/05/2014 |
Africa | |||
Tunisia |
3 |
1 |
01/05/2013 |
Algeria |
2 |
1 |
24/05/2014 |
Asia | |||
Malaysia |
1 |
1 |
08/04/2014 |
Philippines |
1 |
0 |
11/04/2014 |
Americas | |||
USA |
2 |
0 |
01/05/2014 |
Total |
842 |
322 |
|
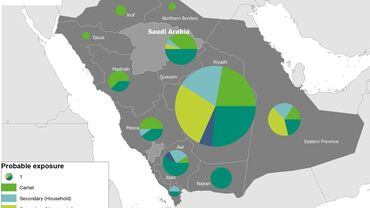
Twenty-one cases have been reported from outside the Middle East. In France, Tunisia, the UK and Iran, there has been local transmission to people who had not travelled to the Middle East, but had been in close contact with laboratory-confirmed or probable cases. Person-to-person transmission has occurred both among family contacts and in healthcare facilities.
All cases have either occurred in the Middle East or have direct links to a primary case infected in the Middle East.
ECDC continues to monitor information on the situation on MERS-CoV worldwide. In earlier Rapid Risk Assessments, ECDC concluded that the risk of importation of MERS-CoV to the EU was expected to continue and the risk of secondary transmission in the EU remains low. The conclusions of the assessment provided in the ECDC rapid risk assessment (RRA) on 2 June 2014 remains valid.
Conclusions
An overall decline of number of cases can be observed in the recent weeks.
More about MERS-CoV