Epidemiological update: Hepatitis A outbreak in the EU/EEA mostly affecting men who have sex with men
Since the last epidemiological update on this multi-country hepatitis A outbreak published on 23 March 2018, 19 European Union/European Economic Area (EU/EEA) countries (Austria, Belgium, Croatia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Portugal, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom) have reported 364 new outbreak-confirmed cases. Outbreak-confirmed cases are EU/EEA residents with laboratory-confirmed hepatitis A virus (HAV) genotype IA and a sequence with ≥99.3% homology to one of the three HAV genotype IA outbreak strains (VRD_521_2016; RIVM-HAV16-090; and V16-25801) based on overlapping fragments at the VP1-2a region.
As of 7 September 2018, the number of outbreak-confirmed cases reported in 22 EU/EEA countries since 1 June 2016 is 4 475 (Figure 1). For 4 411 of these cases, information on gender is available, with a male-to-female (M/F) ratio of 6.8. A sharp reduction in the M/F ratio observed after May 2017, when it reached 11.8. The M/F ratio for the cases reported from May to August 2018 was 4.0. No other strains have been reported to be widely circulating among men who have sex with men (MSM) apart from the three outbreak strains and their close variants (Figure 1).
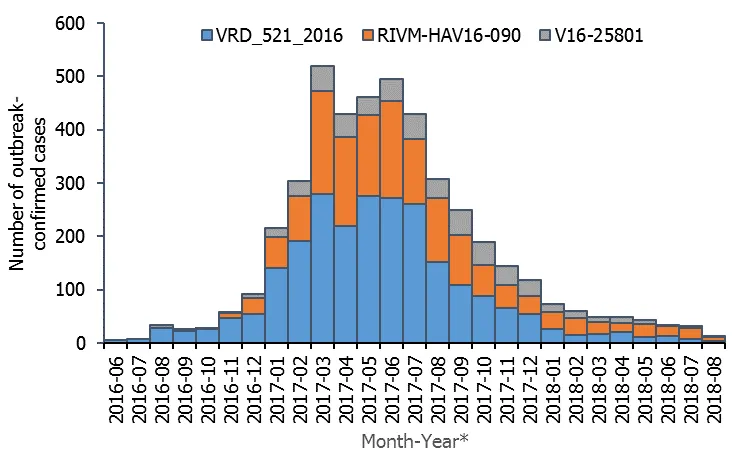
*: Month-Year of report: month of onset; where month of onset was unavailable, month of sampling or receipt by reference laboratory was used.
Countries included: Austria, Belgium, Croatia, the Czech Republic (until March 2018), Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia (until March 2018), Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands (until July 2018), Norway, Portugal, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom.
March 2017 was the month with the largest number of outbreak-confirmed cases (520). There may be substantial reporting delays (weeks or even months) in sequencing information and the number of cases with onset in more recent months is likely to increase once more sequencing results are available. However, the month of the outbreak peak, March 2017, and the following plateau from April to July 2017 are unlikely to change.
Outbreak-confirmed cases provide an underestimation of the true extent of the outbreak. This is because sequencing information is only available for a proportion of hepatitis A cases as sampling strategies vary widely from country to country and during different phases of the outbreak. Between January 2017 and August 2018, 5 537 (22%) of the 25 032 laboratory-confirmed hepatitis A case strains in 24 EU/EEA countries (Austria, Belgium, Croatia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovenia, Slovakia, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom) were sequenced. Of these, 5 537 sequenced cases, 4 217 (76%) were infected with one of the three outbreak strains.
In order to better define the extent of this outbreak, we describe all hepatitis A laboratory-confirmed cases with or without information on genetic sequence and the related male-to-female ratio. From January 2017 to August 2018, the 24 countries mentioned above reported 25 032 laboratory-confirmed cases with an overall M/F gender ratio of 3.0. The M/F ratio from January to December 2017 was 3.6 and from January 2018 to August 2018 1.6. The highest M/F ratio was 4.8, reported from March to May 2017. Since then, the number of male cases decreased progressively until August 2018, when the M/F ratio was 1.4 (Figure 2).
The 19 947 hepatitis A cases reported by the 24 countries from January to December 2017 represent more than a fourfold increase compared with the average of 4 671 cases reported for the same period between 2012 and 2015. Meanwhile, the 5 085 hepatitis A cases reported by the same 24 countries from January to July 2018 (August was excluded because of reporting delay) represent a more than twofold increase compared with the average of 2 258 cases reported for the same months between 2012 and 2015. In both comparisons, 2016 was excluded as the current outbreak was already under way at the time.
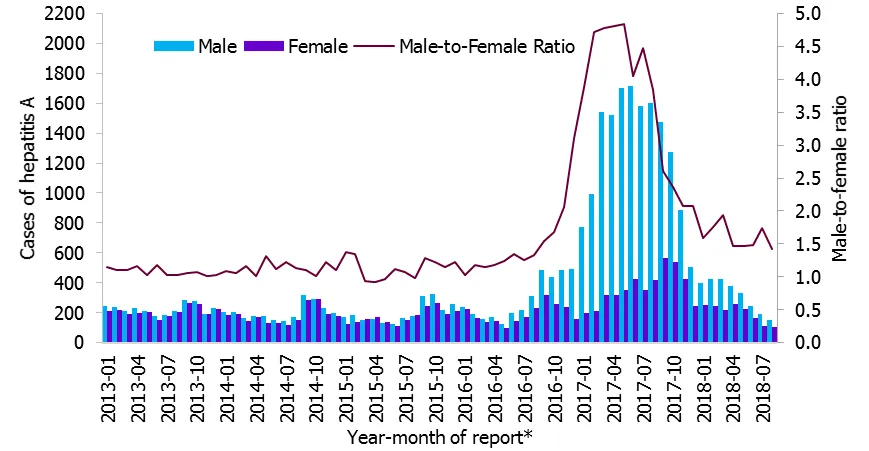
https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2018.23.33.1700641*: Month-Year of report: month of onset; where month of onset was unavailable, month of sampling or receipt by reference laboratory was used.
Countries included: Austria, Belgium, Croatia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia (until March 2018), Lithuania (until July 2018), Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Norway (until March 2018), Poland (information on gender not yet available for 2018), Portugal (until March 2018), Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom (until July 2018). Data from Belgium are missing for 2015 and 2016.
ECDC asked EU/EEA countries to report on events that could contribute to the spread of the outbreak strains in population groups at increased risk of infection or in the community. As a result of these spillover events, particularly during 2017, an increase has been noted in females, children and the elderly in parallel with the large increase in male cases. In recent months, Germany, the Netherlands and Spain reported food-borne outbreaks of hepatitis A associated with one of the three outbreak strains. Since the last epidemiological update, UK-England reported a small cluster of cases in people who inject drugs (PWID).
Publications describing the characteristics of cases in Denmark, France, Germany, Malta, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the EU/EEA are available online.
Vaccination
A main prevention measure in this context is hepatitis A vaccination of MSM and their close contacts according to national recommendations. Groups of MSM at higher risk to be prioritised for vaccination and other options for prevention and control are presented in detail in the latest ECDC rapid risk assessment. Hepatitis A vaccine availability in the EU is currently limited, with certain countries reporting shortages to a lesser or greater extent since the last update, including Denmark, France, Germany and the Netherlands.
It is suggested that vaccination can be promoted and offered to MSM attending pride festivals, where there may be an increased likelihood of contact with hepatitis A-infected individuals. However, limited hepatitis A vaccine availability in some countries may hinder the implementation of these measures.
Since the last ECDC rapid risk assessment in June 2017, Austria, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Norway, Portugal, Spain and the United Kingdom have issued new vaccination recommendations.
Assessment
Between June 2016 and August 2018, 22 EU/EEA countries reported 4 475 hepatitis A outbreak-confirmed cases associated with this outbreak that peaked in March 2017. The number of outbreak-confirmed cases and their distribution in time describes the dynamic of the outbreak, but is also influenced by the different countries’ sequencing strategies. However, the time of the outbreak peak, the plateau from April to July 2017 and the following decrease are not expected to change.
In addition, since January 2017, 25 032 hepatitis A laboratory-confirmed cases were notified by 24 EU/EEA countries. The number of laboratory-confirmed cases peaked in June 2017, while the highest M/F ratio was observed from March to May 2017. As of 7 September 2018, the monthly number of laboratory-confirmed cases is returning to baseline, although still higher than in previous years. The M/F ratio has also strongly decreased in recent months, although remaining higher than in previous years.
Although decreasing in its intensity, after more than two years from the first detection, the outbreak is still ongoing and outbreak strains continue circulating in the EU/EEA, with new cases associated with this event expected in EU/EEA countries in the coming months. Even though it is at a much slower pace than in 2017 and taking into account that part of the cases may be importation events from outside of the EU, the detection of the epidemic strains keeps occurring more often in men than women. In this light, continuing offering hepatitis A vaccination to MSM appears to be an important measure to stop transmission, control this outbreak and prevent future similar events.
The conclusions and options for response set out in ECDC’s rapid risk assessment entitled ‘Hepatitis A outbreak in the EU/EEA mostly affecting men who have sex with men – Third update, 28 June 2017’, remain valid.
See all updates on hepatitis A
Share this page