Epidemiological update: Outbreaks of Zika virus and complications potentially linked to the Zika virus infection, 23 June 2016
New developments since the last epidemiological update
As of 15 June 2016, WHO reports 60 countries and territories with continuing mosquito-borne transmission. Of these, 52 countries and territories have reported autochthonous cases of Zika virus infection during the past nine months. Ten countries have reported evidence of person-to-person transmission of Zika virus, probably via a sexual route. An article on the Zika outbreak in Colombia was published in NEJM on 16 June 2016. Preliminary findings included:
- Overall Zika incidence in women was twice that of men, which reflects factors such as increased testing in reproductive-age women because of the microcephaly threat or the role of sexual transmission.
- More than 90% of mothers who were infected during their third trimesters had given birth, and no infants with microcephaly or brain abnormalities were found.
- Four infants with laboratory evidence of congenital Zika virus disease were born to asymptomatic mothers.
Table 1. Countries and territories with reported confirmed autochthonous cases of Zika virus infection in the past three months, as of 17 June 2016
| Countries | Last case since 3 months |
|---|---|
| American Samoa | Widespread transmission |
| Argentina | Widespread transmission |
| Aruba | Widespread transmission |
| Barbados | Widespread transmission |
| Bolivia | Widespread transmission |
| Brazil | Widespread transmission |
| Cape Verde | Widespread transmission |
| Colombia | Widespread transmission |
| Costa Rica | Widespread transmission |
| Curaçao | Widespread transmission |
| Dominica | Widespread transmission |
| Dominican Republic | Widespread transmission |
| Ecuador | Widespread transmission |
| El Salvador | Widespread transmission |
| Fiji | Widespread transmission |
| French Guiana | Widespread transmission |
| Guadeloupe | Widespread transmission |
| Guatemala | Widespread transmission |
| Guyana | Widespread transmission |
| Haiti | Widespread transmission |
| Honduras | Widespread transmission |
| Jamaica | Widespread transmission |
| Marshall Islands | Widespread transmission |
| Martinique | Widespread transmission |
| Mexico | Widespread transmission |
| Micronesia, Federated States of | Widespread transmission |
| Nicaragua | Widespread transmission |
| Panama | Widespread transmission |
| Paraguay | Widespread transmission |
| Peru | Widespread transmission |
| Puerto Rico | Widespread transmission |
| Saint Lucia | Widespread transmission |
| Saint Martin | Widespread transmission |
| Saint-Barthélemy | Widespread transmission |
| Samoa | Widespread transmission |
| Suriname | Widespread transmission |
| Tonga | Widespread transmission |
| Trinidad and Tobago | Widespread transmission |
| US Virgin Islands | Widespread transmission |
| Venezuela | Widespread transmission |
| Vietnam | Widespread transmission |
| Belize | Sporadic transmission |
| Bonaire | Sporadic transmission |
| Grenada | Sporadic transmission |
| Indonesia | Sporadic transmission |
| Papua New Guinea | Sporadic transmission |
| Philippines | Sporadic transmission |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Sporadic transmission |
| Sint Maarten | Sporadic transmission |
| Thailand | Sporadic transmission |
| Cuba | No |
| New Caledonia | No |
EU/EEA and EU Outermost Regions and Territories
As of 17 June 2016, ECDC has recorded 838 imported cases in 20 EU/EEA countries. The number of imported cases reported is not based on a systematic reporting surveillance system and cannot be considered exhaustive.
EU’s Outermost Regions and Territories:
Martinique: As of 16 June 2016, 30 000 suspected cases have been reported, an increase of 1 070 since last week. The weekly number of cases has been stable over the last four weeks.
French Guiana: As of 16 June 2016, 7 830 suspected cases have been detected, an increase of 290 since last week. The weekly number of cases has been decreasing over the last three weeks.
Guadeloupe: As of 16 June 2016, 13 030 suspected cases have been detected, an increase of 2 840 suspected cases since last week. The weekly number of cases is continuously increasing.
St Martin: As of 16 June 2016, 830 suspected cases have been detected, an increase of 140 suspected cases since last week. The weekly number of cases is still reported as very high.
St Barthélemy: As of 16 June 2016, 70 suspected cases have been detected, an increase of 17 suspected cases since last week. The weekly number of cases is still increasing.
Update on microcephaly and/or central nervous system (CNS) malformations potentially associated with Zika virus infection
As of 15 June 2016, microcephaly and other central nervous system (CNS) malformations associated with Zika virus infection or suggestive of congenital infection have been reported by twelve countries or territories. In the EU, Spain (2) and Slovenia (1) reported congenital malformations associated with Zika virus infection after travel in the affected areas. Thirteen countries and territories worldwide reported an increased incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) and/or laboratory confirmation of a Zika virus infection among GBS cases. Brazil: Between October 2015 and 11 June 2016, Brazil has reported 7 936 suspected cases of microcephaly and other nervous system disorders suggestive of congenital infection; this is an increase of 106 cases since the last update; 1 581 are confirmed cases of microcephaly, 226 of which are laboratory-confirmed for Zika virus infection.
Figure 1. Countries or territories with reported confirmed autochthonous cases of Zika virus infection in the past three months, as of 17 June 2016
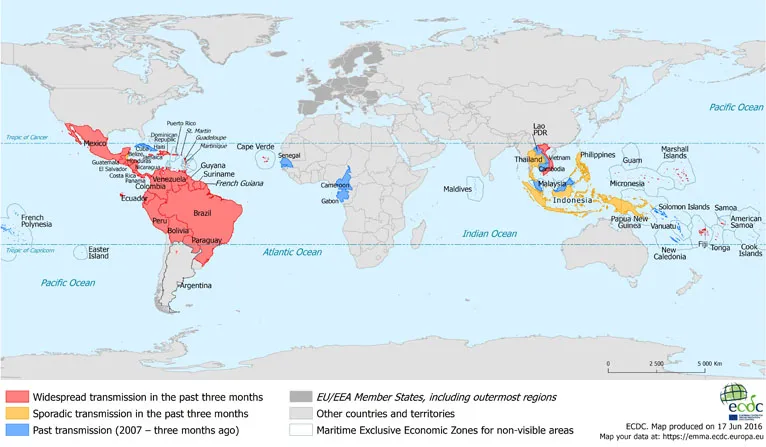
All ECDC maps with information on countries or territories with reported confirmed autochthonous cases of Zika virus infection can be found here.
Related content
Share this page
