Strengthening the public health evidence ecosystem
Infectious disease prevention and control decisions can significantly impact individuals, populations and society. To ensure that public health policies and interventions are sound, decisions must be based on the best available evidence, be scientifically credible, operational, and relevant to the context they are applied to.
While public health agencies are not always the ultimate policy and decision-makers, they play a vital role in enabling informed, timely and effective decisions supported by scientific-based evidence.
'The best available evidence is a cornerstone of public health scientific advice, especially now, as the world faces an unprecedented surge in mis- and disinformation. A strong public health evidence ecosystem, integrating multiple streams and types of evidence, is essential for supporting transparent and sound public health decision-making, and for strengthening trust in science and science-based public health institutions across Europe.' - Piotr Kramarz, ECDC Chief Scientist
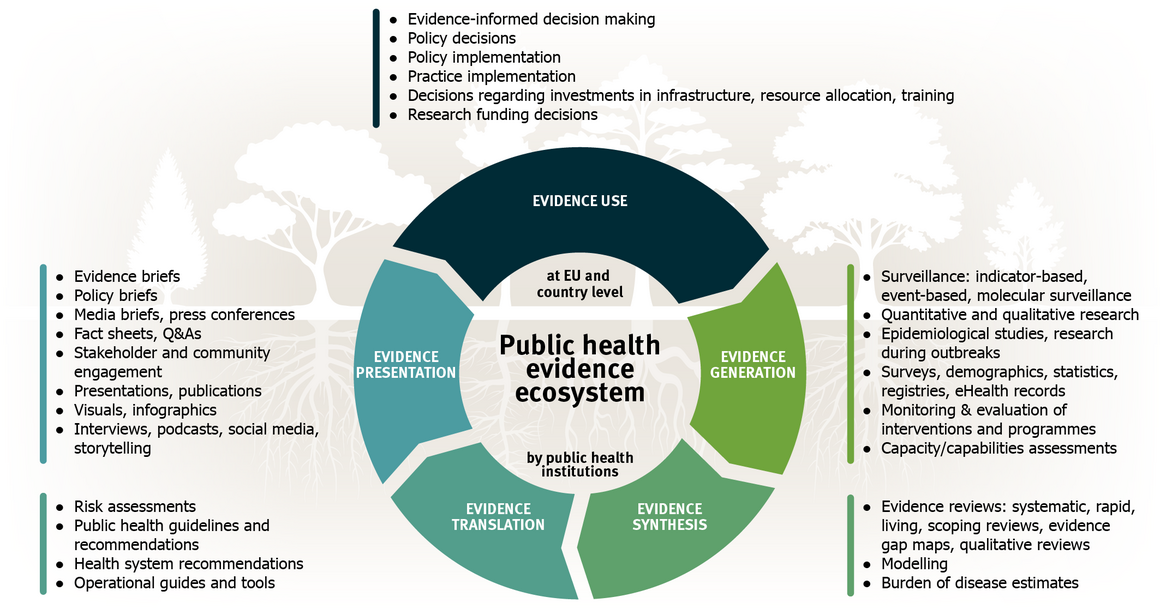
ECDC plays a crucial role in the public health evidence ecosystem by
- coordinating and collaborating with Member States and other partners
- contributing to evidence generation through robust surveillance and applied research and analysis and to evidence synthesis by critically and systematically combining and interpreting findings from different evidence sources
- translating this evidence into clear guidance, risk assessments and public health recommendations
- presenting and communicating findings and recommendations in a way that resonates with decision-makers and the public, ensuring clarity, relevance and accessibility.
The public health evidence ecosystem
- Evidence-informed decision making
- Policy decisions
- Policy implementation
- Practice implementation
- Decisions regarding investments in infrastructure, resource allocation, training
- Research funding decisions
- Surveillance: indicator-based, event-based, molecular surveillance
- Quantitative and qualitative research
- Epidemiological studies, research during outbreaks
- Surveys, demographics, statistics, registries, eHealth records
- Monitoring & evaluation of interventions and programmes
- Capacity/capabilities assessments
- Evidence reviews: systematic, rapid, living, scoping reviews, evidence gap maps, qualitative reviews
- Modelling
- Burden of disease estimates
- Risk assessments
- Public health guidelines and recommendations
- Health system recommendations
- Operational guides and tools
- Evidence briefs
- Policy briefs
- Media briefs, press conferences
- Fact sheets, Q&As
- Stakeholder and community engagement
- Presentations, publications
- Visuals, infographics
- Interviews, podcasts, social media, storytelling
Evidence-based Public Health initiative
ECDC’s Evidence-Based Public Health (EBPH) initiative aims to strengthen the systematic use of evidence in public health decision-making.
An independent Methodological Advisory Group supports the initiative, being composed of external experts, including methodologists and infectious disease and public health experts. Its tasks include
- offering strategic advice to ECDC
- identifying priority areas
- helping raise awareness through public health networks
- ensuring that ECDC’s EBPH initiative meets the needs of the agency and national stakeholders.
The initiative develops user-friendly methodological guidance and tools to support ECDC staff and other public health professionals in applying evidence-based methods and approaches. These materials are developed by a group of four institutions: the Ludwigs- Maximilians- University of Munich, Cochrane Germany, Cochrane Austria and the Norwegian Institute of Public Health. The key priority areas for 2025 are the following:
- Integration of different evidence types and streams
- Elicitation and integration of expert knowledge
- Rapid and ultra-rapid evidence-based public health advice
| Name | Affiliation |
| Koen Blot |
Head of Infectious Diseases Epidemiology, Sciensano (National Public Health Institute), Belgium ECDC Advisory Forum member |
| Céline Dumas | Scientific and International Affairs Division, Santé publique France |
| Mario Fafangel | Head of Regional Office (Nova Gorica) and Public Health Advisor at the Director’s Office, National Institute of Public Health Slovenia (NIJZ) |
| Chantelle Garritty | Prevention Guidelines Division, Public Health Agency of Canada & School of Epidemiology and Public Health (SEPH), Faculty of Medicine, University of Ottawa (adjunct professor) |
| Ágnes Hajdu |
Consultant, National Center for Public Health and Pharmacy, Department of Communicable Disease Epidemiology and Infection Control, Budapest, Hungary ECDC Advisory Forum alternate |
| Otto Helve |
Director of the Department of Public Health, Finnish Institute for health and welfare ECDC Advisory Forum member |
| Henk Hilderink | Principal Expert Public Health Foresight, Centre for Public health, Healthcare and Society, Dutch National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM) |
| Priya Jakhmola | Lead Health Scientist, Guidelines Unit/Office of Scientific Evidence and Recommendations/CDC Office of Science, US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| Tanja Küchenmüller | Unit Head, Evidence to Policy and Impact, Research for Health Department, Science Division, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland |
| Zachary Munn | Professor, Director Health Evidence Synthesis Recommendations and Impact (HESRI), Director Adelaide GRADE Centre, University of Adelaide, Australia |
| Promise Nduku | Director: Evidence synthesis and Learning lab at Elevate Evidence Hub, Johannesburg, South Africa |
| Keith Ian Quintyne |
Consultant in Public Health Medicine sí Health Protection Lead in Evidence Based Medicine, Research & Quality Improvement HSE Public Health: National Health Protection Office, Dublin, Ireland |
| Ana Paula Rodrigues | Coordinator of the Epidemiologic Surveillance and Public Health Observation, Department of Epidemiology of the National Institute of Health Doctor Ricardo Jorge, Portugal |
| Frank Sandmann | Team Lead, Vaccination/VPD Modelling, Robert Koch Institute (RKI), Berlin, Germany |
| Sotirios Tsiodras |
Professor of Medicine and Infectious Diseases at National & Kapodistrian University of Athens Medical School, Chair of National Committee of Public Health experts, Greece |
| Tari Turner |
Professor, Director, Australian Living Evidence Collaboration, Cochrane Australia, School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Australia |
| Rens van de Schoot |
Professor of collaborative Methods in AI and Data Science at Utrecht University in the Netherlands, Methodology and Statistics |
| Karin Wilbe Ramsay |
Project Manager HTA, SBU – The Swedish Agency for Health Technology Assessment and Assessment of Social Services |
Read more
Map of evidence synthesis guidance
An interactive map charting existing methods guidance on evidence synthesis.




